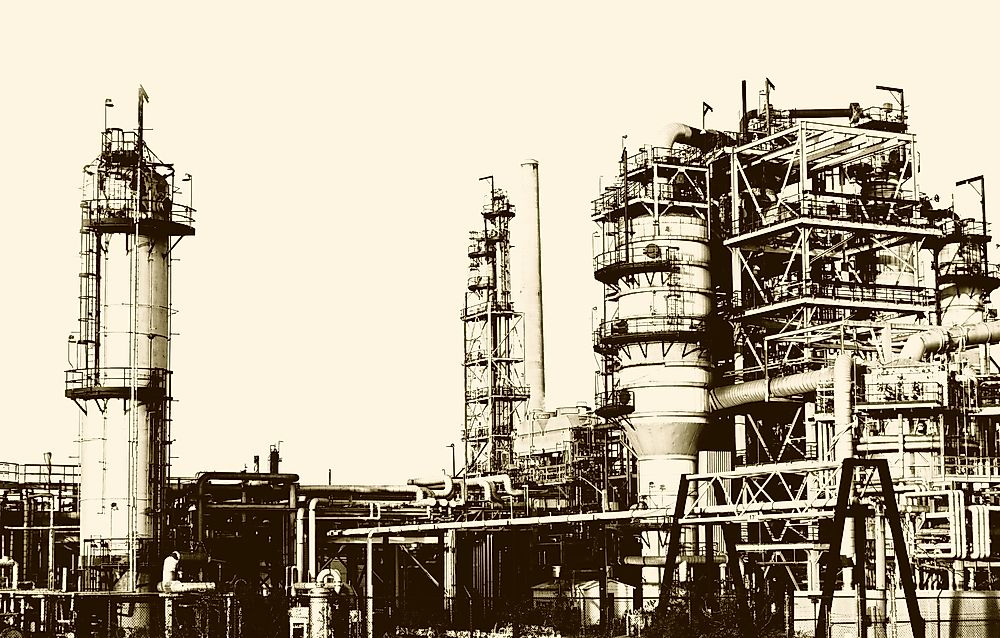



Worries around corporatism are rising and consequently, calls for socialism are becoming louder. There are deep questions around inequality, productivity and regulatory capture. Today, as the world undergoes a profound period of technological change, far beyond what was experienced during the Industrial Revolution, there are some rhymes of history. But its diffusion ended up permeating both, ultimately reshaping political parties before the founding of the Labour Party, representing the culmination of a long debate over the role of capital and rights of workers. Technological transformation took a long time to feed through to politics and policy. As it spread-first to Western Europe and the United States-it also left a much wider mark on the world. Institutions, industry and demography were all to change course and, ultimately, little about life in Britain was left untouched by the Revolution. They disrupted society, upending old structures, as well as building new ones. The innovations that kickstarted the Industrial Revolution fostered modern democracy and led to the foundation of modern economies. Modernity, as we currently understand it, was conceived in England in the mid-eighteenth century. “The Industrial Revolution.” Web Institute for Teachers.“From the American System to Mass Production, 1800–1932: The Development of Manufacturing Technology in the United States.” Johns Hopkins University Press, 1984, ISBN 978-0-8018-2975-8. “Electrifying America: Social Meanings of a New Technology, 1880-1940.” The MIT Press, July 8, 1992, ISBN-10: 0262640309. “Railroaded: The Transcontinentals and the Making of Modern America.” W. “A Nation of Steel: The Making of Modern America 1965-1925.” Johns Hopkins University Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8018-6502-2. “Creating the Twentieth Century: Technical Innovations of 1867–1914 and Their Lasting Impact.” Oxford University Press, 2005, ISBN 0-19-516874-7. “Second Industrial Revolution.” The McGraw-Hill Companies, Feb. In 1886, the first DC (direct current) electric motor was developed, and by 1920, it powered passenger railways in many cities. By replacing the fire hazards of gaslighting, the initial cost of converting to electric lighting was quickly offset by reduced fire insurance premiums. Called “the most important engineering achievement of the 20th century” by the National Academy of Engineering, electric lighting greatly improved working conditions and productivity in factories. By the late 1880s, the first efficient commercial electrical generators made large-scale transmission of electrical power to the public possible. In 1879, famed American inventor Thomas Edison perfected his design for a practical electric lightbulb. He is exhibiting in his hand a replica of his first successful incandescent lamp which gave 16 candlepower of illumination, in contrast to the latest lamp, a 50,000 watt, 150,000 candlepower lamp. Noted inventor Thomas Edison at the lightbulb's golden jubilee anniversary banquet in his honor, Orange, New Jersey, October 16, 1929. By the late 1940s, many of the assembly line factories of the First Industrial Revolution quickly evolved into fully automated factories. Combined with these, the development of machines controlled by rudimentary computers, gave rise to automated production. During the c, newly developed resources like steel, petroleum, and railroads, along with the superior new power source of electricity, allowed factories to increase production to unheard-of levels. While factory automation and productivity had been improved by the limited use of First Industrial Revolution inventions such as the steam engine, interchangeable parts, the assembly line, and mass production, most late 19th century factories were still water-powered.
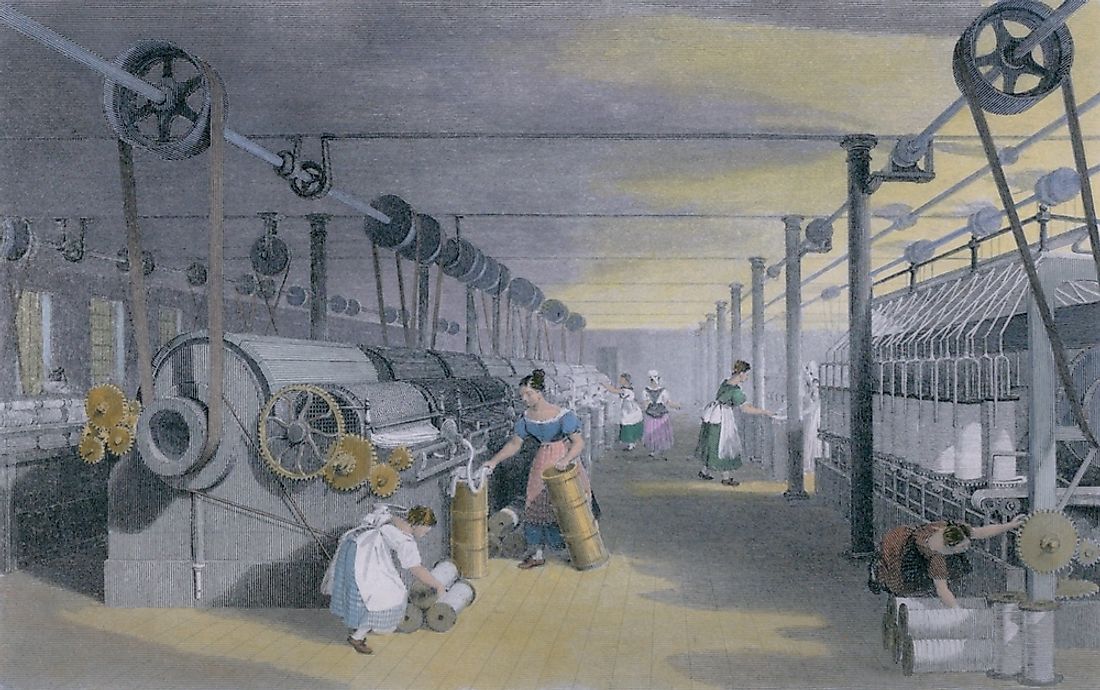

Advancements in factory workflow, such as mass production, electrification, and automation contributed to economic growth.railroad system, the period resulted in an unprecedented increase in industrial production. Considered to have been triggered by the invention of the Bessemer process for the cost-effective production of steel and the associated expansion of the U.S.The Second Industrial Revolution was as period of tremendous economic, industrial, and technological advancement taking place between the end of the American Civil War and the start of World War I.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
